Blog
Why Are Orthopaedic Surgeons at Risk of Noise Induced Hearing Loss?
- Daniel Hastings
Table of Contents
Noise induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a common occupational health condition.
Orthopedic surgeons are at risk of developing noise-induced hearing loss due to continuous exposure to high decibel levels they are exposed to during surgical procedures. Researchers state that the most obvious contributors to noise in the operating rooms include powered instruments, such as saws, drills, and suction devices. These instruments have been documented to generate sounds of 85 to 142 dB and are regularly utilized in orthopedic procedures.
Exposure to these high decibel levels over a prolonged period of time can lead to permanent damage to the inner ear and result in noise-induced hearing loss. To put this into perspective, at 100 (dB), hearing loss is possible after 15 minutes; at 105 9dB), hearing loss is possible in less than 5 minutes; and at 110 (dB), damage can occur in less than 2 minutes!
It is also important for orthopedic surgeons to have regular hearing exams to monitor their hearing health. This will allow them to catch any signs of hearing loss early and to take appropriate steps to protect their hearing.

The Prevalence of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss in Orthopaedic Surgeons
Noise induced hearing loss, or NIHL, is a gradual loss of hearing that occurs as a result of exposure to loud noises. According to the Australian Government Department of Health in Australia, approximately 3.6 million people have some degree of noise-induced hearing loss. More than 1.3 million people live with a hearing condition that could have been prevented. More than 1 in 3 Australians have noise-related ear damage.
While there are many factors that can contribute to this condition (such as genetics), one common cause is prolonged exposure to loud sounds, such as those present in an operating room environment.
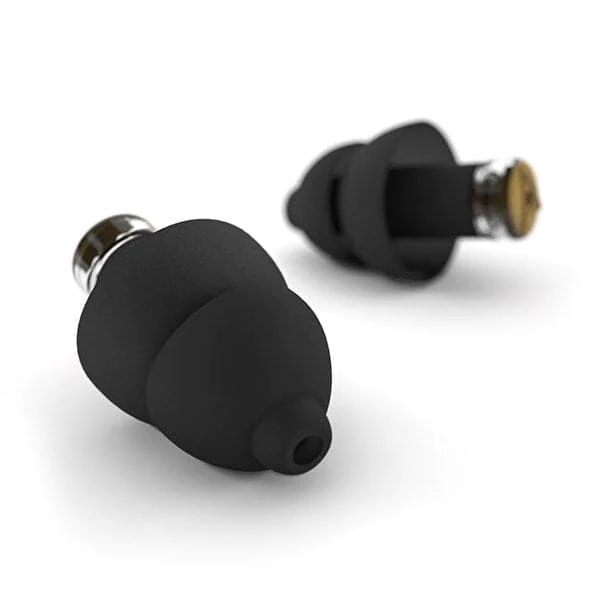
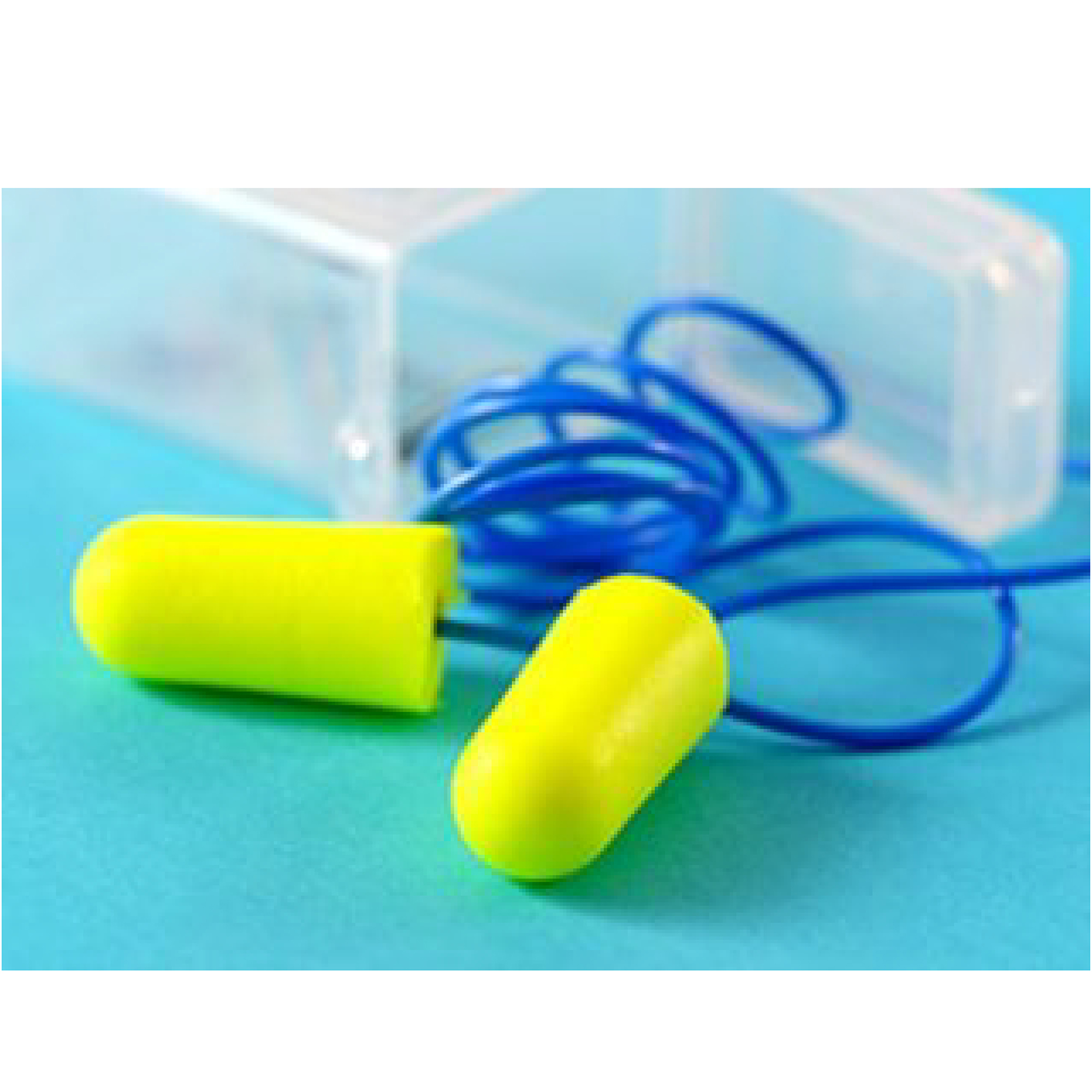
To prevent NIHL, orthopedic surgeons should take measures to protect their hearing. This includes wearing proper hearing protection devices, such as specialized filtered earplugs.
The Australian Society of Orthopaedic Surgeons is considering the issue of occupational noise hazards amid new evidence that orthopedic surgeons experience periods of noise exposure in excess of legal guidelines.
How Much Noise Is Too Loud?
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets the limit for acceptable sound pressure levels at 85 decibels (dB) for eight hours per day over an entire work week; however, this recommendation does not take into account any additional factors like age or gender which may make someone more susceptible than others. In general terms, however: if you have trouble understanding speech when someone speaks directly into your ear, then you might want to consider wearing ear protection when working near machinery like drills or saws!

What is the Cause of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss?
Noise-induced hearing loss is caused by exposure to high decibel levels. Exposure to loud noise can cause permanent damage to the hair cells in your inner ear, which are responsible for sending signals to your brain. This damage can lead to hearing loss.
You should also check: How To Avoid Hearing Loss: 5 Tips To Maintain Ear Health.
The Silence is Deafening
Exposure to loud noise can also cause temporary hearing loss. This type of hearing loss is often temporary, but it can be permanent in some cases.
In his book Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience1, Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi assessed the noise doses endured by surgeons in the operating room. And stated that surgeons, their skilled teams, and their patients were being exposed to a potentially damaging level and sustained dose of sound during the operating day.
What Can be Done to Prevent Noise Induced Hearing Loss?

What Type of Earplugs Should Surgeons Wear?
The best earplugs for surgeons are specialized filter earplugs just like Plugfones Dynamics Hi Fidelity Earplugs. They can be used for more than one surgery, so you don’t have to change them every time you go into the operating room. They are easily cleaned and don’t have any side effects.
Filtered earplugs are different from normal soft foam or silicone earplugs. Unlike standard earplugs that muffle all sound, filtered earplugs such as Earasers have been designed with acoustic filters to lower the decibels equally from high to low frequencies.
They are designed to block damaging sound, preventing tinnitus and hearing loss while still allowing you to hear voices clearly. This is especially important when surgeons need to communicate with each other during an operation. The filters also help protect you from loud noises and other risks associated with the operating room environment.
Takeaway
If you are an orthopedic surgeon, it is important to understand the risks associated with your profession. Hearing loss can be caused by long-term exposure to loud noises and repeated exposure to loud noises. Wearing hearing protection when operating on patients will help prevent noise-induced hearing loss in the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, orthopedic surgeons are at risk of developing NIHL due to the high decibel levels they are exposed to during their daily procedures. To prevent NIHL, orthopedic surgeons should take measures to protect their hearing, such as wearing proper hearing protection devices and having regular hearing exams. By taking these steps, orthopedic surgeons can ensure that they can continue providing high-quality care to their patients without sacrificing their hearing health.
We hope this article has helped you understand the prevalence of noise-induced hearing loss in orthopedic surgeons and some of its causes and prevention methods. If you have any questions about this topic or anything related to hearing health, don’t hesitate to get in touch with us!