Blog
7 Effective Ways to Prevent Tinnitus Issues
- Daniel Hastings
Table of Contents
Tinnitus is a growing problem in our society, with 2.4 million people in Australia suffering from this condition. Tinnitus is characterized by an incessant buzzing, ringing, or humming noise in the ear, which can cause great discomfort, distress, and even depression. The proper ways to prevent tinnitus are important to maintain your ear health.
In this post, we will discuss what tinnitus is, the importance of hearing protection, how to avoid tinnitus, and how it feels to have tinnitus. Tinnitus prevention is possible with the right hearing protection.
What is Tinnitus?

Tinnitus is a condition characterized by the perception of noise or ringing in the ears, often without an external source. This sound can be described as buzzing, ringing, humming, hissing, or whistling, and it can be constant or intermittent. Some people experience tinnitus in one ear, while others experience it in both.
It can be a symptom of an underlying issue such as hearing loss, ear injury, or circulatory system disorders.
There are different types of tinnitus:
1. Subjective tinnitus is the most common type, and it is caused by damage to the auditory system. The damage can be caused by exposure to loud noise, ear infections, wax buildup, medication side effects, and more.
2. Objective tinnitus is caused by a physical sound source, such as a blood vessel or muscle spasm.
3. Pulsatile Tinnitus sounds in sync with the heartbeat. Often related to blood flow or vascular issues.
4. Non-pulsatile tinnitus is continuous or intermittent sound. Not synchronized with the heartbeat.
5. Somatic Tinnitus is the perception of noise that is affected by body movements. It may be linked to muscle contractions or joint problems.
6. Neurological Tinnitus is related to disorders of the nervous system. It can involve the auditory pathways in the brain.
How Is Tinnitus Diagnosed?

Tinnitus diagnosis involves a comprehensive assessment to identify underlying causes and determine appropriate treatment.
The process typically includes:
- Detailed information on health, medications, and tinnitus characteristics.
- A thorough check of ears, head, neck, and neurological system.
- Measures hearing sensitivity to identify associated hearing loss.
- MRI or CT scans for visualizing the ear, brain, and surrounding structures.
- Checks for underlying medical conditions contributing to tinnitus.
- Assess inner ear and auditory nerve function.
- Questionnaires and interviews to understand emotional impact.
- Vestibular or angiography tests for specific aspects related to tinnitus.
7 Ways How to Prevent Tinnitus
You can prevent tinnitus with the help of the following guidelines:
1. Noise Protection
To prevent tinnitus, use ear protection in loud environments. Limit exposure to loud music, machinery, and recreational activities. Earplugs or earmuffs can safeguard your hearing and reduce the risk of tinnitus.
2. Volume Control
Keep audio devices at a moderate volume. Avoid prolonged use of headphones or earphones at high levels. Be mindful of loud noises in your surroundings, and maintain a healthy distance from sources of excessive noise.
3. Regular Hearing Check-ups
Schedule regular hearing check-ups to detect and address potential hearing issues early on. Timely identification of hearing loss can prevent the development of tinnitus and other related conditions.
4. Stress Management
Chronic stress can contribute to tinnitus. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises. Maintaining a balanced lifestyle and managing stress can positively impact your health and reduce tinnitus risk.
5. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopt a healthy lifestyle by exercising regularly, maintaining a balanced diet, and staying hydrated. These factors contribute to overall well-being and may help reduce the risk of developing tinnitus or worsening existing symptoms.
6. Ear Hygiene
Keep your ears clean and dry. Avoid inserting objects into your ears, as this can damage the delicate structures inside. Proper ear hygiene reduces the risk of infections and complications that may lead to tinnitus.
7. Limit Medication Risks
Certain medications, like ototoxic drugs, can contribute to tinnitus. Consult with healthcare professionals before taking medications, and be aware of potential side effects. Discuss alternative options if you have concerns about the impact on your hearing.
How Is Tinnitus Treated?

You can not treat tinnitus completely, but by following different ways, you can reduce the symptoms of tinnitus.
1. Sound Therapy Devices
Sound therapy is a common approach to managing tinnitus by using external sounds to mask or distract from the internal tinnitus noises.
Various sound therapy devices are available:
White Noise Machines: These devices produce a constant background noise that helps drown out or reduce the perception of tinnitus sounds. Users can adjust the volume and tone to find the most effective masking effect.
Nature Sounds and Relaxation Tapes: Sounds of nature, calming music, or relaxation tapes can be used to provide a soothing environment and divert attention away from tinnitus. These are often incorporated into sound therapy sessions.
Hearing Aids with Sound Generators: Many modern hearing aids come equipped with built-in sound generators. These devices amplify external sounds and may include customizable options for additional sound therapy. The amplification of ambient noise can help mask tinnitus.
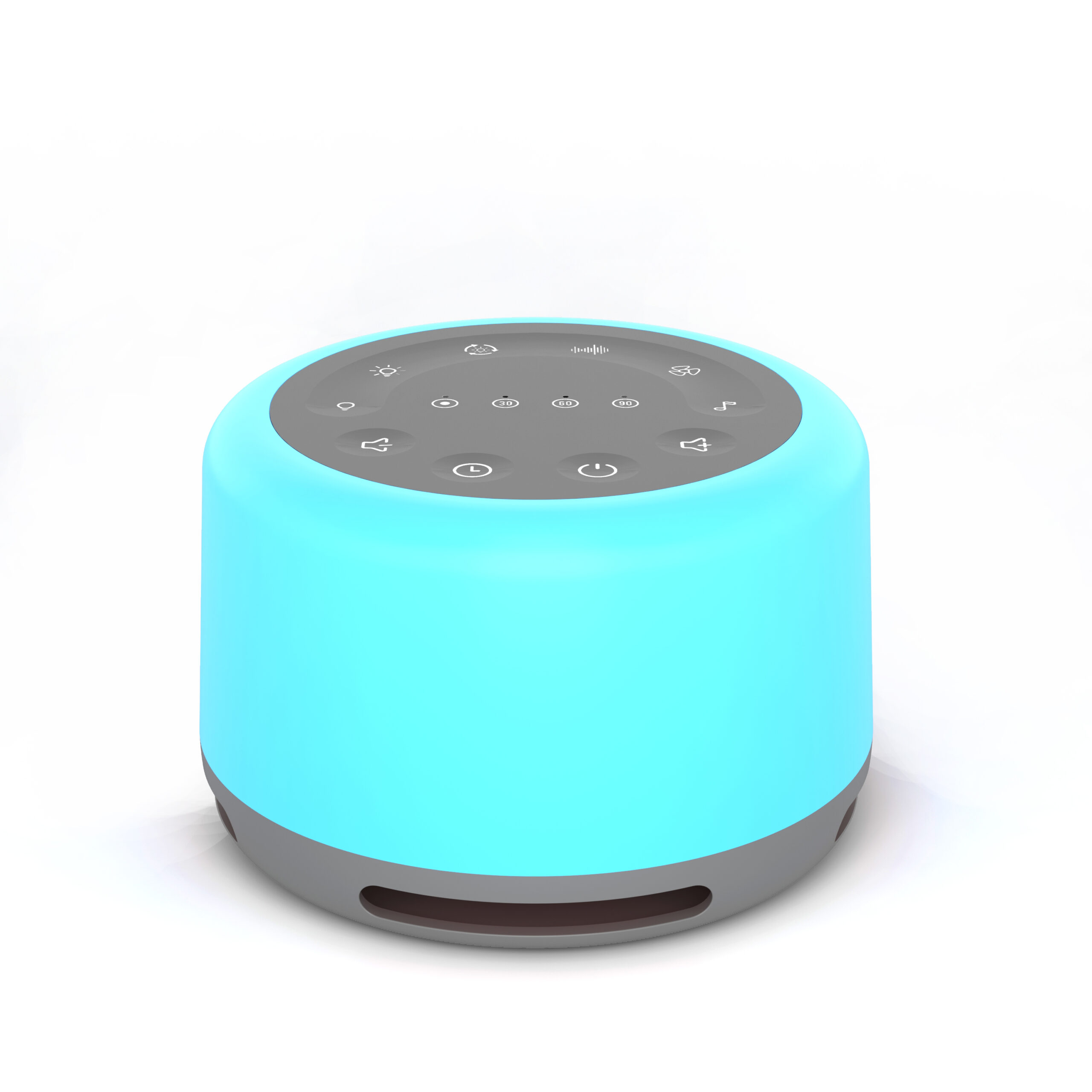
Tabletop Sound Machines: Portable sound machines that emit a variety of soothing sounds. These devices are convenient for creating a calming atmosphere at home or the workplace.
Customized Sound Apps: Smartphone apps offer customizable soundscapes for tinnitus relief. Users can choose from a range of sounds and create personalized combinations to suit their preferences.
2. Medications
While there is no specific medication to cure tinnitus, certain drugs may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms or address underlying causes:
Tricyclic Antidepressants: Tricyclic anti-depressants help to manage tinnitus symptoms, especially when associated with depression or anxiety. These drugs may have side effects, so careful monitoring is necessary.
Benzodiazepines: These anti-anxiety medications are used to provide temporary relief from tinnitus-related stress and anxiety. Prolonged use is generally avoided due to the risk of dependence.
Antidepressants (SSRIs/SNRIs): Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may be prescribed to address the emotional impact of tinnitus and manage associated symptoms.
Anticonvulsants: In some cases, medications like anticonvulsants are considered to manage tinnitus, especially if it is related to neural hyperactivity.
Vasodilators: If tinnitus is linked to vascular issues, medications that improve blood circulation.
What are the Possible Complications of Untreated Tinnitus?
If the tinnitus remains untreated, it may cause several complications:
- Sleep disturbances
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Difficulty concentrating
- Increased stress levels
- Impaired cognitive function
- Reduced quality of life
- Hearing difficulties
- Social isolation
- Negative impact on work performance
When is Tinnitus a Medical Emergency?

You need to get help from a doctor if tinnitus becomes a medical emergency. Sudden hearing loss, especially if it occurs after head trauma or exposure to loud noises. Unilateral tinnitus with facial weakness, pulsatile tinnitus with severe headaches, and tinnitus with vertigo require urgent attention.
Persistent tinnitus in one ear, particularly in children, demands immediate evaluation to rule out serious conditions. Sudden onset in individuals with cardiovascular risk factors and unexplained changes in tinnitus should also prompt swift medical assessment. Any unexpected or severe alterations in tinnitus, especially when coupled with other symptoms, necessitate prompt attention to identify and address potential underlying emergencies.
FAQs
Can You Live a Long Life with Tinnitus?
Yes, individuals can live a long and fulfilling life with tinnitus. While there may be challenges, effective management strategies and coping mechanisms can improve quality of life.
Does Tinnitus go Away?
Tinnitus may resolve on its own, especially if linked to temporary factors like earwax or medication. However, persistent cases often require management rather than a complete disappearance.
Is Tinnitus Permanent?
Tinnitus can be permanent, especially if associated with age-related hearing loss or underlying medical conditions. Effective treatment focuses on managing symptoms rather than achieving a complete cure.
Conclusion
Tinnitus is a growing problem in our society, and it is essential to take steps to protect our hearing to avoid this condition. With the help of earplugs, earmuffs, and taking regular breaks from noisy environments, we can reduce our risk of developing tinnitus.
If you do suffer from tinnitus, it is important to talk to your doctor to identify the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan. With the right support, you can learn to manage your tinnitus and reduce its impact on your quality of life.