Blog
Understanding the Causes and Effects of Snoring
- Daniel Hastings
Table of Contents
Understanding what causes snoring is essential since people snore for various reasons. Once you understand why you snore, you can find the right solutions for a quieter, deeper sleep for you and your partner.
What Causes Snoring?
It’s no secret that bedtime snoring can wreak havoc on a relationship. Tempers can easily flare when one person is constantly snoring and keeping the other up all night. But what causes snoring in the first place?
There are several contributing factors that can cause a person to snore. Snoring is sometimes a result of age, sinus, allergies, smoking or colds, and cases of flu.
For others, it can be the anatomy of their mouth, larger tongue or tonsils, and thicker, softer palates that can cause obstruction to the airways. Snoring can commonly be a consequence of sleep deprivation.
How Does Snoring Affect?
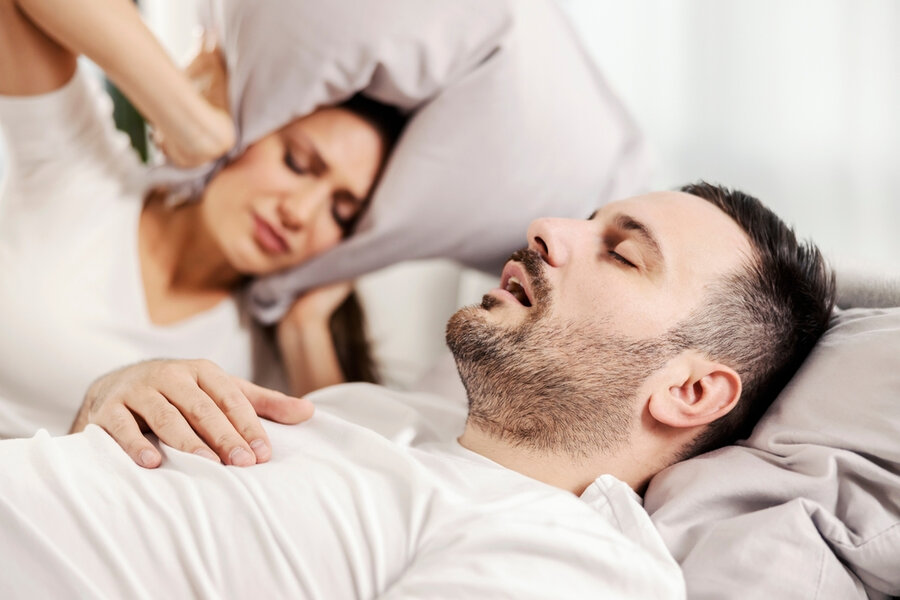

Snoring is a common condition that can affect anyone. However, it is more common in men than women and more prevalent in overweight people. If you’re concerned that you or your partner may be snoring too much, talk to your doctor about possible solutions.
Several treatments, including lifestyle changes and devices that help keep the airways open, are available. At some point in their life, just about everybody will snore, and it’s usually not something to worry about, but it can be a chronic issue for some people, a problem that requires attention. It may sometimes indicate a severe health condition as well.
Snoring can not only affect your own quality of sleep, but it can also be disturbing to your partner and their well-being.
Snoring occurs when, during sleep, you can’t move air freely through your nose and throat. This is because the muscles in your neck, the roof of your mouth, your throat, and your tongue have become relaxed. As you breathe in air while sleeping, the surrounding tissue in the throat vibrates, generating the familiar sound of snoring.
What is Sleep Apnea?
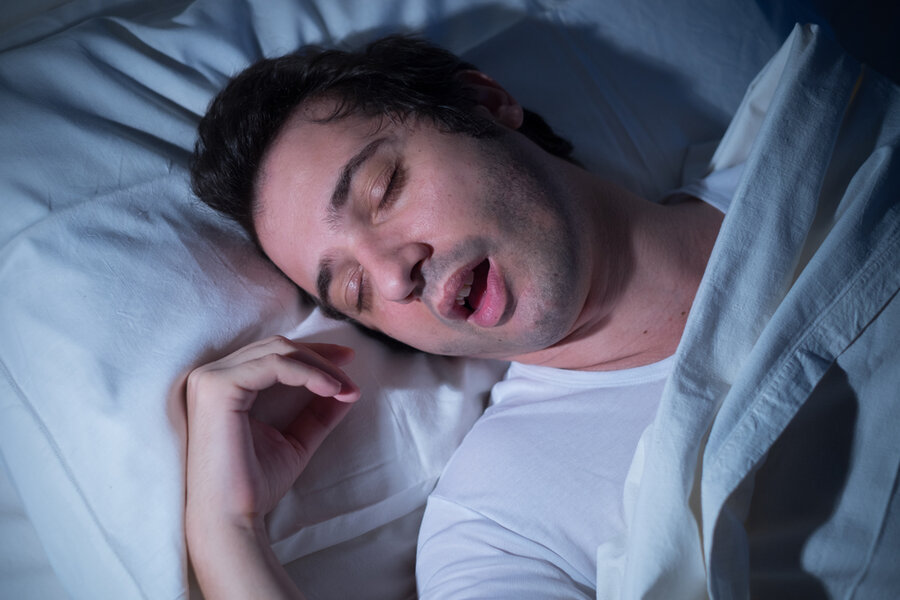

A sleep disorder called obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is often associated with snoring. Sleep apnea is a possible serious sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops for brief periods during sleep.
Changes in lifestyle, such as weight loss, avoiding alcohol near bedtime, or sleeping on your side, can help stop snoring.
To no one’s surprise, the largest group of snorers are middle-aged and older men. Thirty percent of adults over the age of 30 snore, and women represent one-third of those snorers; snoring is more prevalent than most people realize.
How to Treat Sleep Apnoea?
Is There a Cure for Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnoea? To treat your snoring, your doctor likely will first recommend lifestyle changes, such as:
- Nasal Breathing Device
- Losing weight
- Avoiding alcohol close to bedtime
- Treating nasal congestion
- Avoiding sleep deprivation
- Avoiding sleeping on your back
- Quit smoking
Moreover, there are medical devices and surgery available that can decrease disruptive snoring. These, however, are not appropriate or necessary for everyone who snores. Talk to your doctor if you are overly sleepy during the day if you snore frequently or significantly loudly, or if your partner notices that sometimes you completely stop breathing.
Treating sleep apnoea will help you achieve a better night’s sleep (and more likely your partner’s sleep too) and may decrease the chances of other health side effects.
For mild cases of sleep apnoea, you can try sleeping on your side, the use of a pillow or wedge can help keep you from rolling on your back through the night. Changes in lifestyle, such as weight loss and or avoiding alcohol near bedtime are very often what will remedy snoring and or sleep apnoea. Other options that may help alleviate symptoms include avoiding sleeping tablets and quitting smoking. Some people find that nasal decongestant sprays can help also.
For more moderate cases of sleep apnoea, we recommend the use of a nasal breathing device. The Airmax nasal breathing device is a super cost-effective, natural, and unobtrusive way to help prevent snoring while you are sleeping. The Airmax nasal breathing device is a soft, small nasal stint made of medical-grade silicone, that helps open the nasal passage creating an increased area for airflow to help get oxygen into the lungs.
The positive effects of nasal dilators, such as Airmax have been scientifically proven and Airmax represents a powerful device to improve nasal breathing and represents a good alternative for corrective surgery of deviated septum and similar endonasal procedures.
What Are The Main Causes of Snoring?
Most people snore occasionally, and it’s usually not a cause for concern. But if you snore regularly, it could be a sign of a more serious problem. Snoring occurs when airflow is blocked as you breathe. The tissues in the back of your throat vibrate when air rushes past them, which causes the snoring sound.
There are several things that can cause snoring, including obesity, smoking, and alcohol use. Sleeping on your back can also make snoring worse. If snoring is a problem for you, talk to your doctor. There are treatments available that can help reduce or eliminate snoring.
Read on to discover the main causes of snoring.
1. Ageing
Snoring increases with age. As we get older, it’s not just our bones and joints that can become weaker – our muscles, including around our airway and soft palate can start to deteriorate.
This can cause snoring, as the tongue and throat muscles are unable to keep the airway open properly.
However, there are ways to help combat this problem through myofunctional therapy and mouth and throat exercises. By strengthening the muscles in this area, myofunctional therapy can help reduce snoring caused by weak muscles.
2. Weight
Being overweight or obese means you have more fat around your neck. Neck fat compresses the upper airway, especially when lying down, making it narrower and snoring more likely to occur.
Snoring and being overweight isn’t only about neck fat.
Being overweight and snoring isn’t just about neck fat. Snoring and sleep apnea worsen when people have central fat, fat around the chest and or belly.
Midriff fat pushes up your diaphragm, squeezing your ribcage, thus shrinking your lung capacity. This is a common occurrence in pregnant women.
3. Alcohol
Alcohol consumption is often a cause of snoring. The more you drink, the louder and heavier your snoring will become.
This is because alcohol relaxes the muscles in the back of the throat, which can lead to obstruction of the airway. When the airway is obstructed, air is forced through the narrow opening, causing the tissues to vibrate and produce the characteristic sound of snoring.
The more alcohol someone drinks, the more relaxed their muscles will become, and the louder their snoring will be.
In some cases, alcohol consumption can also cause people to snore when they otherwise would not.
4. Breathing
The more you breathe through your mouth, the higher the chance that snoring will occur. It’s because the walls of your throat at the back of your mouth vibrate easily, while those in the nose don’t.
When your mouth breathes, the air directly hits the back of your throat and causes the soft tissues to vibrate. If you find that your mouth breathes at night, there are a few things you can do to prevent it. First, make sure that your nasal passages are clear by using a nasal breathing device for snoring, such as the Clipair Nasal Device.
You can also try sleeping with a humidifier, such as the Crane Ultrasonic Cool Mist Humidifier in your room to keep the air moist and your throat lubricated. And finally, you could try to prop up your head with an extra pillow to prevent mouth breathing. By taking these steps, you can reduce your chances of snoring at night.
5. Illness/Sinus Congestion
When you experience symptoms of a sinus infection or other issues, such as a blocked nose, you will be forced to breathe through your mouth, which will make snoring more likely.
Further, the increased pressure in your throat from having a blocked nose causes it to become narrower and harder for air to flow – this could lead to not just sleeping problems but other health issues like asthma.
6. Back Sleeping
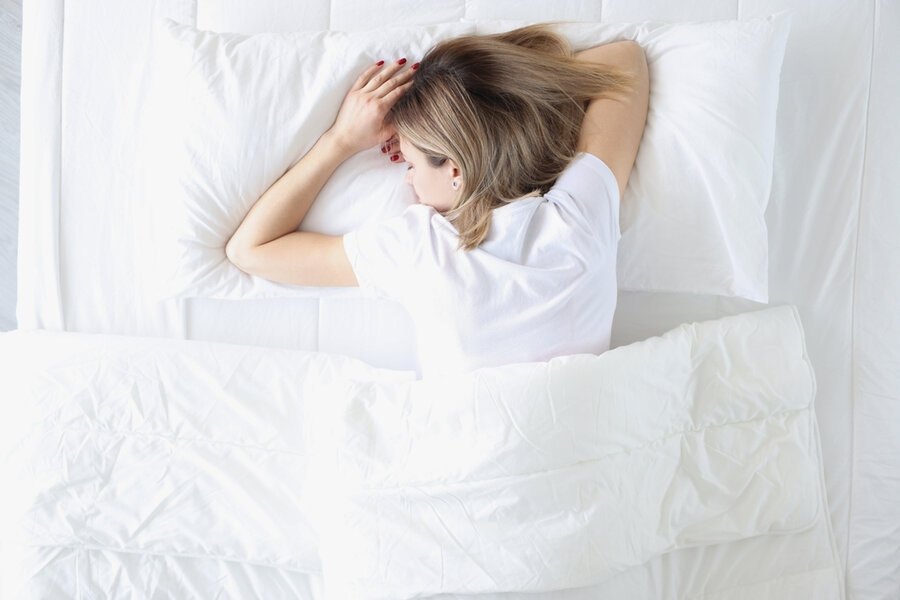

Sleeping on your back can make it harder to breathe. The weight of the tongue falls directly down, blocking airflow and causing snoring problems. It is time for you to start sleeping on your side – if you can’t maintain this, it is time for you to invest in a snoring aid like the Oscimed Anti Snoring Belt that will help prevent this from happening.
7. Nasal Polyps
Polyps are growths of the mucosa, or soft tissue that often develop in the nasal cavity and sinuses. They can range in size from tiny and insignificant to large and irritating. Polyps can cause snoring by blocking the airway.
Many polyps go unnoticed, especially in children, some can cause problems with breathing, infection, inflammation, and snoring.
Cigarette smoke is a major cause of inflammation, and smokers are more likely to develop polyps. Following a visit to your doctor, they may recommend a visit to an Ear Nose, and Throat Specialist (ENT). A nasal endoscope can spot polyps and be removed surgically if necessary.
8. Allergies
The link between snoring and allergies, hay fever, or smoking has been long-standing. People who suffer from these conditions often experience worse breathing problems, leading them to even more restless sleep than before due to a lack of oxygen going through the nasal passageway.
In addition, it’s thought that allergens increase inflammation in our airways, making obstructions deeper and thus harder for enough airflow throughout all areas.
9. Medication
When you take certain medications, your throat muscles can relax, and this can make it difficult for you to sleep. This is particularly more so with sleeping tablets, anesthetic drugs, oral steroids, and epilepsy drugs.
10. Hereditary
Research shows that snoring can be genetic.
Hereditary snoring may be caused by genetic, physical features, including a narrow throat, receding chin, small jaw, large tongue, or large, soft palate. Hereditary snoring may also be linked to other health conditions, such as obstructive sleep apnoea. If you think you may have hereditary snoring, talk to your doctor.
11. Pregnancy
Pregnancy is a time of many changes, both physical and hormonal. One common side effect of these hormonal changes is snoring.
Hormones cause the blood vessels to dilate and the mucous membranes to swell, leading to congestion and a narrowing of the nasal passages. This forces you to breathe through your mouth as you sleep and more often than not, snore.
While snoring during pregnancy is relatively common, it can annoy you and your partner. If snoring is a problem for you during pregnancy, there are some things you can do to help ease the symptoms.
Some simple lifestyle changes, such as sleeping on your side instead of your back, can make a big difference.
You can also try using a humidifier or saline nasal spray to moisten your nasal passages. If snoring persists despite these measures, talk to your doctor about other options, such as positional therapy devices or mouthguards.
With a little effort, you can help reduce or eliminate snoring during pregnancy and get a good night’s sleep for both you and your baby.
Snoring and Sleep Deprivation
Sleep is one of THE most important functions of the human body! It allows the body to rest and recover from the day’s activities.
Sleep deprivation is the condition of not having adequate duration and/or quality of sleep. Without sufficient sleep, our brain and body lack mental performance and health support. Sleep deprivation can lead to daytime sleepiness, poor concentration, irritability, an increased risk of accidents, anxiety, and depression.
In the long term, it can also contribute to major health problems such as obesity, heart disease, and stroke. If you think you may be sleep-deprived, we can help to improve your sleep habits.
Summary
In conclusion, you can do many things to prevent mild snoring, please see your doctor if you snore frequently; we define what causes snoring. Snoring control will help you sleep better and will enhance your quality of life. Your doctor will review your signs and symptoms and your medical history to diagnose your condition. Your doctor will also carry out a physical examination.
An imaging test, such as an X-ray, a computerized tomography scan, or magnetic resonance imaging, may be requested by your doctor. These tests check your airway structure for issues, such as a deviated septum.
Giving our nerves a break implies that we feed them the minimum possible stimulation and maximize rest to prevent snoring.
We at Sleep and Sound help people every day to get a better night’s sleep, if you’d like to chat in person with one of our friendly team members, we are just a phone call away.